Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is an innovative, non-invasive treatment that has gained popularity in recent years, especially for mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. But how effective is TMS, and what can patients realistically expect? This article provides a comprehensive look at TMS effectiveness, explores how it works, and examines its impact on specific conditions like anxiety and depression.
What is TMS and How Does It Work?
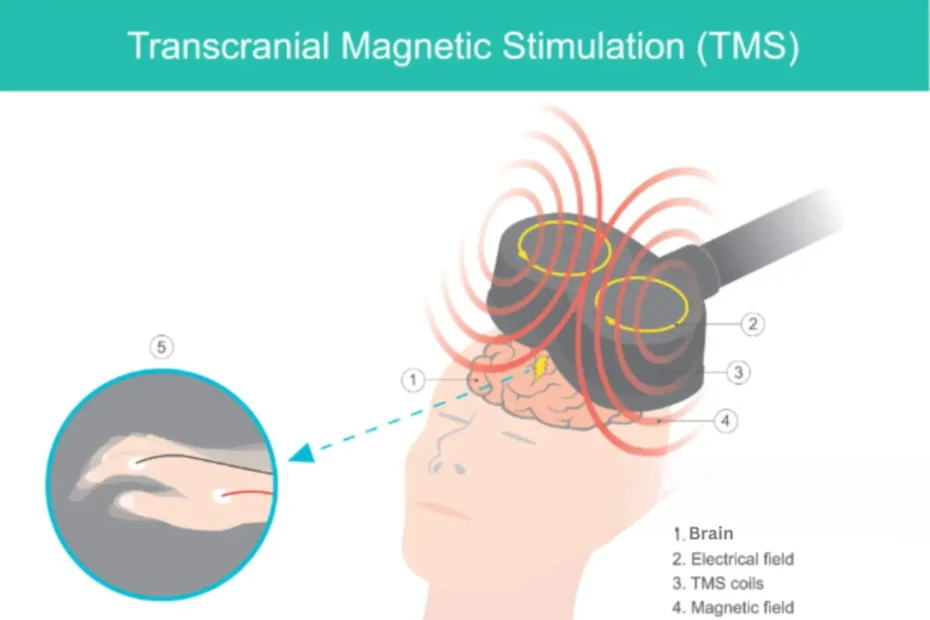
TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation) uses magnetic pulses to stimulate areas of the brain associated with mood regulation, particularly targeting the prefrontal cortex. Unlike other treatments, TMS does not require surgery, anesthesia, or the ingestion of medications.
Sessions are generally well-tolerated, with patients sitting in a comfortable chair while a magnetic coil is placed near their head. Each session usually lasts between 20 to 40 minutes, with a typical treatment course involving daily sessions over four to six weeks.
Why People Consider TMS Treatment
TMS is often considered after other treatments, like medications or therapy, haven’t provided enough relief. Its non-invasive nature and minimal side effects make it a suitable option for patients who have struggled with traditional treatments.
How Effective is TMS for Depression?
One of the most common applications for TMS is in treating major depressive disorder (MDD). Studies over the past two decades have shown promising results for TMS treatment effectiveness in helping people with depression.
Clinical Evidence on TMS for Depression
Clinical studies reveal that TMS is effective for many patients with treatment-resistant depression. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that around 50-60% of patients who had not responded to antidepressant medications showed significant improvement after completing a TMS course. About 30-35% of these patients achieved full remission, meaning their depressive symptoms were no longer present.
The effectiveness of TMS treatment for depression varies among individuals, but these statistics indicate that TMS can be highly beneficial for those with limited treatment options. It’s also worth noting that TMS provides lasting relief for some individuals, with many patients reporting improvements that continue for months after treatment.
How Effective is TMS for Anxiety?
Although TMS is primarily used to treat depression, there is a growing interest in its application for anxiety disorders. TMS for anxiety is somewhat less established than for depression, but early studies show encouraging results.
TMS and Anxiety: What Studies Show
A meta-analysis published in Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment analyzed TMS’s impact on patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The review found that TMS improved anxiety symptoms for a majority of patients, although the level of improvement varied.
Some studies suggest that the effectiveness of TMS treatment for anxiety may be influenced by the specific brain regions targeted, as well as the frequency and intensity of the magnetic pulses.
While more research is needed to determine how effective TMS is for anxiety, current evidence suggests that it may provide an alternative for those who haven’t found relief from other treatments.
Factors Affecting TMS Effectiveness
While TMS has shown positive outcomes, its effectiveness can depend on a range of factors. Here are some key elements that influence TMS effectiveness:
1. Condition Being Treated
As noted, TMS is particularly effective for depression, but its success rate varies for other conditions. Research on how effective TMS is for anxiety continues to grow, but it is not as robust as data for depression. Conditions like OCD, bipolar disorder, and PTSD are also being studied, with some promising preliminary results.
2. Patient’s Response to Past Treatments
Patients with treatment-resistant depression are typically the ones who benefit most from TMS. However, the degree of treatment resistance can affect results; those who have had multiple failed treatments may have a lower response rate to TMS than those with fewer prior treatments.
3. Number of Treatment Sessions
For most people, TMS requires consistent sessions to see lasting results. Typically, a full course includes 20-30 sessions. Research indicates that patients who complete the recommended course tend to see greater improvements than those who undergo fewer sessions.
4. Targeted Brain Regions
The effectiveness of TMS can also depend on the specific brain areas being targeted. For example, targeting the left prefrontal cortex has been found to yield better results in reducing depression symptoms. Some studies are exploring whether targeting other areas of the brain might increase TMS treatment effectiveness for anxiety or other conditions.
5. Individual Variability
No two patients respond to TMS in exactly the same way. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and brain chemistry can all play a role in determining how effective TMS is for an individual.
TMS Treatment: Benefits and Limitations
While TMS has many advantages, it’s essential to weigh both the benefits and limitations when considering TMS effectiveness.
Benefits of TMS Treatment
- Non-Invasive and Medication-Free: TMS doesn’t involve surgery or require patients to take daily medications.
- Minimal Side Effects: Most side effects of TMS are mild and temporary, including scalp discomfort and mild headaches.
- Proven Results for Depression: With evidence supporting how effective TMS is for depression, TMS has been FDA-approved as a treatment for this condition.
- Potential for Lasting Results: Many patients experience lasting relief from symptoms, with some individuals reporting improvements for several months after their last session.
Limitations of TMS Treatment
- Effectiveness Can Vary: TMS doesn’t work for everyone, and its effectiveness may depend on individual factors.
- Availability and Cost: TMS therapy can be expensive and may not be covered by all insurance plans.
- Time Commitment: Completing a full course of TMS requires a time commitment, often involving daily sessions over several weeks.
Is TMS Effective for Other Conditions?
While depression is the primary condition treated with TMS, researchers are exploring its use for various other mental health issues and neurological conditions.
TMS for OCD
TMS has received FDA approval as an adjunct treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Studies show promising results, with many patients reporting symptom improvement. However, results can vary, and more research is needed to determine the full potential of TMS for OCD.
TMS for PTSD
Research into TMS for PTSD is ongoing. Initial studies suggest that TMS may help reduce symptoms in some PTSD patients, though outcomes are not as established as those for depression. Targeting specific brain areas associated with trauma responses may be the key to increasing TMS effectiveness for PTSD.
FAQs: TMS Effectiveness and What to Expect
Here are some common questions people have when considering TMS and its effectiveness.
1. How long does it take to see results with TMS?
Many patients begin to notice improvements after about two weeks of treatment, though it can vary. Some may see results sooner, while others might require the full course to experience benefits. The full impact of TMS is often realized several weeks after completing treatment.
2. Is TMS effective for everyone?
While TMS has helped many patients with treatment-resistant depression, it isn’t effective for everyone. Studies show around a 50-60% response rate for depression, with a smaller percentage achieving full remission. Individuals interested in TMS should discuss their medical history and expectations with a healthcare provider to assess if TMS is likely to benefit them.
3. How effective is TMS for anxiety compared to depression?
TMS has a more established success rate for depression than for anxiety. Studies indicate that TMS may help with anxiety symptoms, particularly when these are secondary to depression. However, how effective TMS is for anxiety specifically varies and often requires different treatment protocols than those used for depression.
4. Does TMS have side effects?
TMS is well-tolerated by most people, with the most common side effects being mild headaches and scalp discomfort at the site of the magnetic coil. These side effects are typically temporary and lessen as treatment progresses.
5. How does TMS compare to medication for treating depression?
TMS offers an alternative for individuals who don’t respond to antidepressant medications or prefer a medication-free treatment. Studies suggest that TMS treatment effectiveness can be similar to antidepressants for certain individuals, particularly those with treatment-resistant depression.
Final Thoughts: Is TMS Effective for You?
TMS offers an alternative to traditional treatments, especially for individuals with depression who haven’t found relief through medications or therapy alone. While TMS effectiveness is most well-documented for depression, research continues into its potential for anxiety, OCD, and other conditions.
Ultimately, how effective TMS is depends on multiple factors, including the condition being treated, individual patient characteristics, and adherence to the full treatment course. Consulting with a qualified healthcare provider is essential to determine whether TMS is the right fit and to discuss realistic expectations for treatment outcomes.
Whether you’re considering TMS for depression, anxiety, or another mental health issue, understanding the benefits, limitations, and effectiveness of TMS treatment can help you make an informed decision about your mental health journey.